Have you heard the saying, “The more things change, the more they stay the same?” Yeah, Screw that cliché. Change is good.
Introduction: The Dawn of Web 3.0
2010 saw the release of WEB 3.0, a new and improved version of the internet.
An improvement of Web 1.0 and Web 2.0
In October 1990, Tim Berners-Lee introduced the first version of the world wide web, known as Web 1.0 and the first website editor/browser (WorldWideWeb.app), among the three key technologies that formed the basis of the internet:
- HTML: HyperText Markup Language, the markup or formatting language of the web
- URI or URL: Uniform Resource Identifier or Locator, a unique address used to identify each resource on the web
- HTTP: HyperText Transfer Protocol, which allows for the retrieval of linked resources from across the web3
Web 1.0 was the age of static webpages retrieved from servers and was dominated by large companies such as Yahoo, AOL, and MSN. The focus of Web1.0 was content creation and the primary way of delivering content was through HTML (Hypertext Markup Language). Web 1.0 was all about the publishing of information. Users were not able to interact with content, or even create their own content.
Web 2.0 is the second generation of the World Wide Web that is focused on the ability for people to collaborate and share information online. The term was first coined in 1999 by Darcy DiNucci.
The web 2.0 movement has enabled the creation and proliferation of web-based applications, such as web-based document collaboration, web-based project management, web-based data management, dynamic webpages, social networks, and user-generated content. With web2.0 it is possible for users to interact with content, share it, and even create their own content. The focus of web2.0 is user engagement and the primary way of delivering content is through AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML).
So, what changed in Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 is the third generation of the internet and is based on the decentralization of data and the use of blockchain technology.
Blockchain is a distributed digital ledger technology that is used to securely, openly, and permanently record and preserve data. It is a growing collection of records known as blocks that are connected and safeguarded by encryption. Each block typically includes transaction information, a timestamp, and a cryptographic hash of the previous block. Blockchain is a secure and dependable means to store and transport data since it is resistant to data modification and tampering by design.
Thinking of the internet as a city and blockchain technology as city infrastructure is a great analogy for defining Web 3.0.
The blockchain is like a central component of the city — an immutable ledger that holds all data on all data within its network. And just as a city endures even if its hosting site closes down or changes hands, this immortal chain endures over time and allows for iterations from any given point in time to be found.
In addition to being more efficient, safe, and private than the existing web, Web 3.0 allows for the seamless interchange of information and value between people and machines. It is anticipated to enable technologies like artificial intelligence and the Internet of Things as well as the creation and deployment of Decentralized Applications (DApps) and Smart Contracts by users, allowing them to interact peer-to-peer without the need for an intermediary.
Unlike conventional web applications, decentralized applications (dApps) do not store or are governed by a single company and enable users to exchange value and data without central authority.
Smart contracts, that are used to automate machine-to-machine transactions, are another feature of Web 3.0 that lets users create and carry out contracts without the aid of an intermediary. Finally, blockchain technology gives consumers more control over their data and the capacity to conduct anonymous and secure online transactions by enabling the creation and management of digital identities.
To Summarize: The Key Features of Web 3.0
- 1. Decentralization: Web 3.0 relies on a decentralized architecture; thus, data is not controlled by a single, centralized node. Instead, data is spread out among several nodes, enhancing security and resilience
- 2. Interoperability: Web 3.0 will make it possible for many applications to interact and access data on the same platform
- 3. User-Centricity: Web 3.0 was created with the user as the focal point of the interaction. Users will consequently have greater control over their data and be free to select the applications they wish to use
- 4. Semantic Web: Web 3.0 will leverage the Semantic Web, Applications will be able to better interpret user inquiries and provide more accurate and customized results as a result
- 5. Artificial Intelligence: Web 3.0 will be enhanced by AI, enabling more sophisticated data processing and search results
- 6. Blockchain Technology: One of the fundamental elements of Web 3.0 will be blockchain technology. Users will be able to verify transactions as well as store and transfer data securely thanks to this.
Will Web 3.0 Kill SEO?
In 2010, in an interview at the O’Reilly Solid conference, Tim Berners-Lee discussed his thoughts on Google’s role in the transition to semantic web. He emphasized thatGoogle will not survive the semantic Web in its current state.
Nowadays, as Web 3.0 is all about Semantic Web and other advanced features as mentioned before, the statement “Google will not survive the Semantic Web” is being used as a baseline for many clickbait titles. Let’s look at that statement closer so we can separate the wheat from the chaff.
What is Semantic Web?
The Semantic Web is a concept that’s been around for nearly two decades. It’s essentially an extension of the current internet where information is stored in a way that can be understood by machines as well as humans. Information is given context and meaning through tags and metadata to allow machines to better understand the content being presented and make connections between related information.
What is a Semantic Search Engine?
Semantic search engines interpret the context of a search query to better understand the meaning of the search term and the relationships between entities. Semantic search is different from keyword-based search because it considers not only the keywords in a document, but also how words are used together to determine which documents should be included in the results.
Lee argued that search engines would need to be more intelligent, relying on semantic analysis of the web content to provide more meaningful search results. He also suggested that the Semantic Web would allow for more natural language processing, which would enable more intuitive interactions with search engines. Additionally, he noted that the Semantic Web would need to rely on more data sources for better search results, and that companies like Google would need to adapt and integrate with these data sources.
So, to summarize, according to Lee, Google search needs the following improvements to survive the semantic web era:
- Be Intelligent
- Rely on semantic analysis of the web content
- Be able to process natural language
- Be able to process intuitive interactions with search engines
- Rely, adapt, and integrate on more data sources for better search results
Since Lee made his arguments, it seems that someone at Google used Lee’s article as a cookbook and executed an accurate work plan accordingly: Google already started implementing the changes later in 2010.
Google’s Journey to a Semantic Search Engine
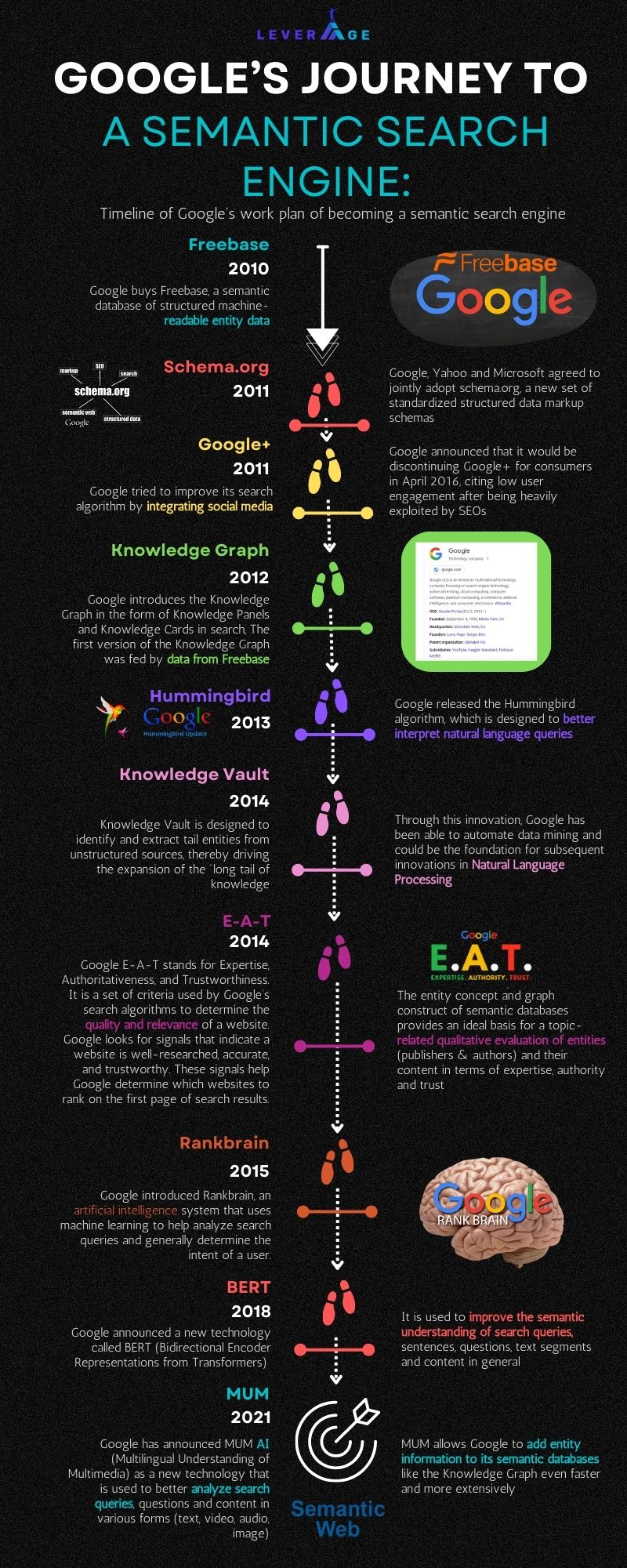
So Semantic Web will not kill SEO as we know it. The basic principles of SEO still apply and Google Search as well as other search engines will still be powerful tools.
But What if People Stop Searching on Google?
The internet is dominated by centralized search engines like Google, Bing, Baidu. But what if there was a way to break this monopoly? Well, there may very well be…
In the Web 3.0 era, it is not unlikely that Individual users will wield power over traditional search engines through a peer-to-peer network of participants. This works similarly to torrenting, where reliable storage is provided, content cannot be censored, and access to content can be arranged in the absence of reliable connection.
Moreover, as Web 3.0 technology continues to evolve, new search engines that offer a more decentralized and secure experience emerge.
New Type Search Engines
Let’s start by clarifying the difference between a blockchain search engine and a decentralized search engine.
A blockchain search engine / block explorer is a search engine for a blockchain network. It allows users to search for information contained within a blockchain ledger, including transactions, blocks, and other data. Blockchain search engines are used to provide the public with access to information contained within a blockchain and to make the process of searching for data easier and more efficient.
Decentralized search engines are an alternative to the traditional search engines like Google. These search engines do not store a copy of the data on their servers but instead rely on the network of computers that make up the peer-to-peer network to store and index content. In this way, no one entity has control over what is indexed and displayed in search results.
There are many different decentralized search engine platforms. They vary in their features, but most of them use blockchain technology to achieve their goals.
Unlike traditional search engines, which employ opaque indexing mechanisms, decentralized search engines do not need crawler bots to be used to gather information about changes made to content on a site because all changes update in search results automatically.
Decentralized search engines feature a public database with open access for everyone. Whereas traditional search engines feature centralized databases with limited access to the public.
Decentralized searches give users full control over their privacy settings across all platforms at all times. Their privacy settings cannot be changed without their consent, which means there is no way for anyone else to access your data without your explicit permission.
The lack of centralization means that there’s no one point of failure — if one node fails, it won’t have any effect on other nodes within the network. The distributed nature of this approach also means that there are no central servers or backends that can be attacked by hackers or compromised by governments looking for information about their citizens. access to content can be arranged in the absence of reliable connection and the risk of censorship or loss of privacy is eliminated.
Here are some examples of decentralized search engines:
YaCy – a free, decentralized peer-to-peer search engine that anyone can use to build a search portal for their intranet or to help search the public internet.
Presearch – a decentralized search engine that rewards community members with Presearch Tokens (PST) for their usage, contribution to, and promotion of the platform.
Cyber – an open source, decentralized search engine that uses artificial intelligence to index the internet.
Will Decentralized Search Engines Become Popular?
There are reasons why there is a distinct possibility that decentralized search engines could become popular. For one, it increases privacy. It would be much more difficult to censor and control content. This is particularly important in countries where governments have tried to suppress information or manipulate news. A decentralized search engine would also be resistant to censorship and can be used as a tool for freedom of speech.
The second reason is they give people much greater control over their data.
And finally, the fact that people can get paid for searching could create an entire new income stream for many people and could go a long way towards boosting popularity of decentralized search engines.
It should be also mentioned that decentralization, as an idea, is growing in popularity every day thanks to cryptocurrencies.
Therefore, yes, there is at least a significant chance that decentralized search engines could become popular sooner than we think.
Centralized search engines VS Decentralized search engines

What Would Become of SEO if Google Search Became Decentralized
Can Google be Decentralized?
Yes, Google’s services can be decentralized.
Google’s services are currently centralized, meaning they are hosted on Google’s centralized servers. However, Google could also offer decentralized versions of their services, where the data and infrastructure are hosted on decentralized networks rather than centralized servers. Decentralized versions of Google services could be created using blockchain technologies, decentralized cloud storage, and peer-to-peer networks.
Google’s search results are based on what they perceive as the best results for a given search query. The algorithm is a proprietary and not open to public scrutiny. A decentralized search engine would not be able to control its results in this manner.
If Google search engine were to become decentralized, it would have an extremely negative impact on SEO because it would make it almost impossible for Search Engine Optimization tactics to be effective. Without the centralized power of Google, there would be no single authority to determine the most effective practices for Search Engine Optimization. Additionally, it would be difficult to track and measure the success of SEO campaigns due to the lack of a single authoritative source.
SEOs would need to make sure their content is optimized for all search engines. This could include optimizing content for specific search engines, using appropriate keywords and phrases, and ensuring content is formatted correctly. Additionally, monitoring performance of content would be across multiple search engines efforts are providing the desired results.
Let’s Talk about the Elephant in the Room: What about ChatGPT?
As of December 13, 2022, ChatGPT is shaking the search world. Will it revolutionize search as we know it? Let’s find out.
ChatGPT is a natural language search engine powered by GPT-3 (Generative Pre-trained Transformer 3) technology that combines the best elements of chat and search, based on a natural language processing (NLP) model developed by OpenAI. It is trained on a large dataset of conversations and now able to answer any query you might have while generating realistic responses tailored to the context of the conversation. ChatGPT can also be used to search for data, images, videos, and more
ChatGPT has the potential to revolutionize search by enhancing results with better understanding of the user’s intent and answer with more accurate, relevant information. It could also reduce the amount of time it takes to find solutions by providing more natural language processing capabilities that can understand more complex queries.
ChatGPT Search VS Google Search
To make a long story short, ChatGPT may be mastering natural language processing, but Google is still the master of search. Google has been trying to master natural language processing for some time. It’s had a few successes and has even taught computers how to understand human speech, but Google’s NLP is just one of the many areas where it excels in search.
To start with, Google provides search results from the whole web, updated to date. ChatGPT data and events are limited, dating up till 2021.
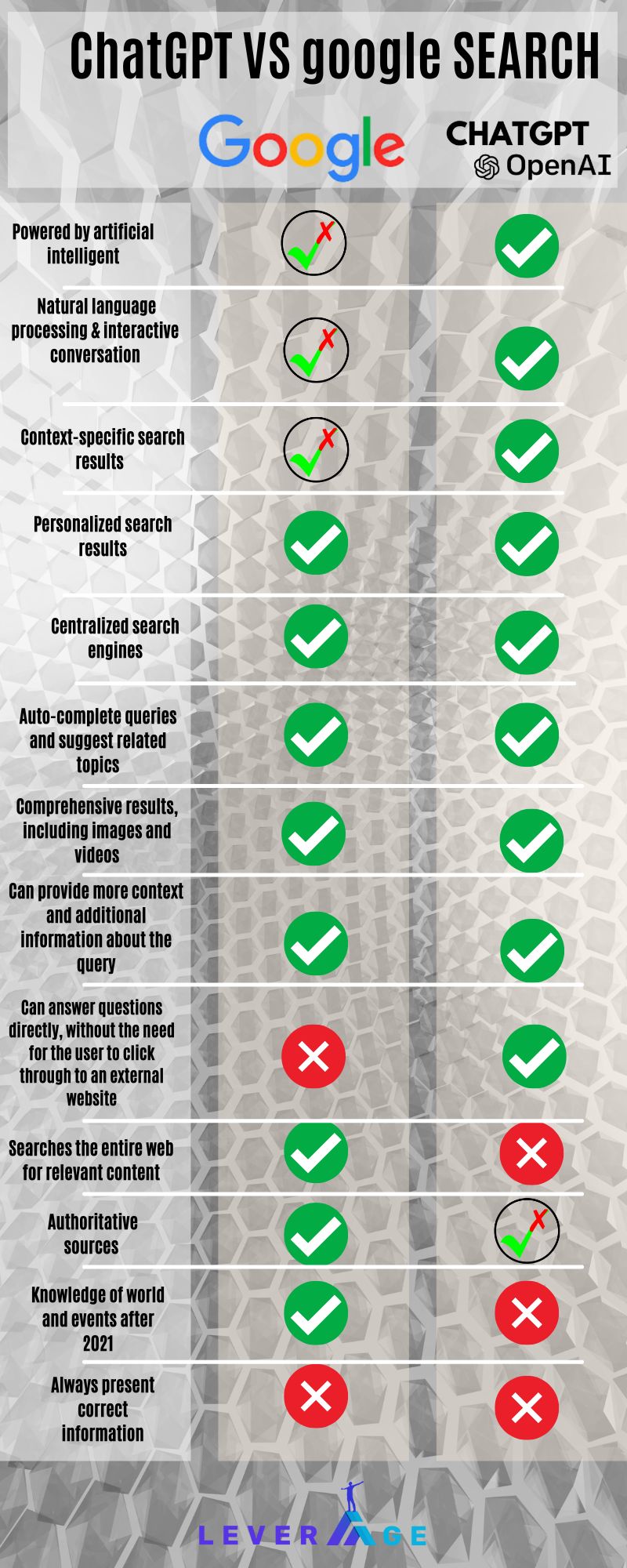
How Could ChatGPT Impact Traditional SEO?
In the short run, ChatGPT can have a positive impact on Search Engine Optimization as it can be used to create more engaging content with natural language processing technology that can help improve website rankings and visibility on traditional search engines.
In the long run, although ChatGPT is far from being perfect, it has the potential to attract some of Google’s traffic and reduce search volumes on Google and others alike, but while ChatGPT could potentially be used to improve search results, it is not a direct competitor to Google search and is not likely to replace it.
Summary and Takeaways
– We believe traditional SEO will maintain its relevance and importance for now. At this point, search engines are not being replaced as web3 technology is still in its infancy and has yet to be widely adopted.
-Decentralized search engines will gain popularity over time and will change SEO over time.
-Search will evolve to a Hybrid solution that will include decentralized search engines and Centralized search engines and content distribution choices will be decided by the users.
-We anticipate consolidation of expertise technologies such as ChatGPT and search engines to bring in enhanced and new abilities to search soon. That would be the big change for the SEO community
– Marketers should research and adjust to new monetization models to meet and utilize Web3 new opportunities and platforms
Marketers should research and adjust to new monetization models to meet and utilize Web3 new opportunities and platforms
To sum up, exciting times are ahead of us, new opportunities abound, and sharpened practices will be put to the test.
We at Leverage are excited to be at the forefront of this new frontier in digital marketing. Our team of experts has been trained in the most current Web 3.0 technologies, and we are eager to put our skills to work for you.
Contact us today and let’s get things moving





